The Trump Administration has signaled that it plans to expand energy production, expedite energy permitting, and ‘roll-back’ regulations and practices that impede growth. As part of this effort, Mr. Trump has named Lee Zeldin, a former GOP member of Congress, to lead the EPA.
Mr. Trump has stated that Mr. Zeldin wishes to “ensure fair and swift deregulatory decisions” while maintaining “the highest environmental standards, including the cleanest air and water on the planet.’’ Further, Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, heads of the so-called Department of Government Efficiency, or DOGE, have vowed to work with the Trump Administration to use executive action “to pursue three major kinds of reform: regulatory rescissions, administrative reductions and cost savings.”
Tag: environment
WOTUS Redefined Again!

By: John B. King
The Supreme Court’s ruling in Sackett v. EPA continues to dominate discussions regarding the scope of jurisdiction over adjacent wetlands. Now, the Corps and EPA seek to codify that ruling into the regulatory definition of ‘waters of the United States.’
In Sackett, the Supreme Court adopted Justice Scalia’s opinion in its prior Rapanos decision. It held that the Clean Water Act extends only to those wetlands that are as a practical matter indistinguishable from waters of the United States. The Corps must establish first, that the adjacent body of water constitutes ‘waters of the United States’ (i.e., a relatively permanent body of water connected to traditional interstate navigable waters) and second, that the wetland has a continuous surface connection with that water, making it difficult to determine where the water ends and the wetland begins. Sackett v. EPA, 143 S.Ct. 1322, 1341 (20243).
Continue reading “WOTUS Redefined Again!”EPA’s Regulatory Roll-Back
In March 2025, Administrator Zeldin announced that EPA will reconsider a number of regulations in order to advance various executive orders issued by President Trump and fulfill EPA’s own Powering the Great American Comeback Initiative. These efforts include the 2024 ambient air standard for particulate matter, the 2009 endangerment finding, and the scope of jurisdiction over ‘adjacent wetlands after the Supreme Court’s 2023 decision in Sackett.
In the Biden Administration, EPA lowered the National Ambient Air Quality Standard for particulate matter, the PM 2.5 NAAQS. The standard was reduced to levels that were close to background levels in some areas. EPA announced it is “revisiting” the lower standard because, among other things, the lower standard “raised serious concerns from states across the country and served as a major obstacle to permitting.”
Continue reading “EPA’s Regulatory Roll-Back”The Fading Luster of Carbon Capture
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is used to carbonate beverages and enhance plant growth. It has also been used for decades in enhanced oil recovery, in which CO2 is injected into oil- or gas-bearing formations to help extract oil and gas. Of course, many say that CO2 causes or contributes to climate change / global warming. In 2009, EPA issued its ‘endangerment finding’ in which EPA determined that current and projected concentrations of CO2 and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere threaten the public health and welfare of current and future generations.
The idea of capturing CO2 before it enters the atmosphere and using it or injecting it for perpetual storage, or sequestration, came about as a way to mitigate the anticipated impacts of climate change. To facilitate carbon capture, use, and storage (CCUS), Congress created the 45Q tax credit in the US Tax Code. Additionally, the Biden Administration touted CCUS as an important tool to address climate change. Even the prior Governor of Louisiana included it as a centerpiece of his climate strategy.
Continue reading “The Fading Luster of Carbon Capture”What A Difference A Single Memo Makes!
The scope of jurisdiction over wetlands under the Clean Water Act has long been debated and litigated. The Supreme Court and other courts have issued various rulings explaining and limiting the scope of such jurisdiction. The Corps of Engineers (Corps) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), though, have not always strictly adhered to those rulings and have sought to expand their jurisdictional reach. Now, the Trump Administration seems determined to force compliance with those rulings.
Continue reading “What A Difference A Single Memo Makes!”The Push To Unleash American Energy
On January 20, 2025, the day of the inauguration, President Trump signed Executive Order 14154, Unleashing American Energy. Through the EO, President Trump seeks to “encourage energy exploration and production on Federal lands and waters … in order to meet the needs of our citizens and solidify the United States as a global energy leader long into the future.” He ordered an immediate review of “all existing regulations … and any other agency actions … to identify those agency actions that impose an undue burden on the identification, development, or use of domestic energy resources.” He further ordered that agencies must “expedite permitting approvals” to achieve this overall goal.
The relevant federal agencies have heard the call. Doug Burgum, the Secretary of the Interior, issued Order No. 3418 to implement the EO. In it, Secretary Burgum ordered steps be taken to reduce “barriers to the use of Federal lands for energy development” and that leases cancelled during the Biden Administration be reinstated. Chris Wright, the Secretary of the Department of Energy, criticized net-zero policies, stating that they threaten the reliability of our energy system and achieve “precious little in reducing global greenhouse gas emissions.” He resumed consideration of pending applications to export American liquefied natural gas (LNG). Towards that end, he announced a new export authorization for the Commonwealth LNG project proposed for Cameron Parish, Louisiana and provided an export permit extension for Golden Pass LNG Terminal, currently under construction in Sabine Pass, Texas
EPA is also involved. Administrator Zeldin announced an initiative, titled Powering the Great American Comeback, which included his ‘five pillars’ approach. The ‘pillars’ include Restoring American Energy Dominance and Permitting Reform, Cooperative Federalism, and Cross-Agency Partnership. Energy produced in America “is far cleaner than energy produced overseas” and is better for the environment because “we do it better here.” However, the cost and length of time to obtain necessary permits is a potential impediment to achieving these goals. EPA will “bring down that timeline [to] make sure it doesn’t take as long to get a permit.”
Administrator Zeldin also announced that EPA will reconsider over thirty regulations. These include the standards of performance for oil and gas facilities (Subparts OOOOb/c) and the effluent limitations guidelines and standards (ELGs) for wastewater discharges for oil and gas extraction facilities. EPA will also reconsider regulations on power plants (the Clean Power Plan 2.0).
Overall, though, perhaps the most important one is the reconsideration of the 2009 Endangerment Finding and all of the regulations and actions that rely on it. In the Endangerment Finding, EPA concluded that carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and other greenhouse gases threaten public health and welfare. While the Finding itself did not impose any requirements, it was a “prerequisite for implementing greenhouse gas emissions standards for vehicles and other sectors.” Secretary Wright stated that the Finding “has had an enormously negative impact on the lives of the American people. For more than 15 years, the U.S. government used the finding to pursue an onslaught of costly regulations – raising prices and reducing reliability and choice on everything from vehicles to electricity and more.”
In addition to its regulatory impact, EPA provided other reasons for the reconsideration. First, when EPA announced the Finding, it indicated that, by itself, it did not impose any costs and that EPA could not consider future costs when making the Finding. However, EPA has subsequently relied on the Finding as part of its justification for certain regulations with an aggregate cost of more than one trillion dollars. Second, the Finding itself acknowledged significant uncertainties in the science and assumptions used to justify the decision but EPA has never sought comment on major developments in innovative technologies, science, economics, and mitigation that may impact the Finding. Finally, major Supreme Court decisions, including Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo, have provided new guidance on how EPA should interpret statutes to discern Congressional intent and ensure that its regulations follow the law.
EPA, and the other federal agencies reviewing their existing regulations and prior actions to implement the EO, must exercise some caution in changing policies. In very general terms, an agency must indicate an awareness that it is changing position, show that the new policy is permissible under the statute, indicate that the new policy is better, and provide reasons for adoption of the new policy. In light of Loper Bright, an agency would likely have to show that the new policy is not just permissible but in line with the ‘best reading’ of the statute. Overall, the agency must provide a reasoned explanation for the change. They must also follow the Administrative Procedure Act. To amend or revoke a rule, notice and comment are required and decisions are subject to judicial review. The reconsideration process will take some time and the outcome is not at all certain due to the ongoing threat of litigation.
An increased emphasis on the domestic production of oil and gas and a decline in regulatory burdens are certainly welcome to the oil and gas industry and those related industries that depend on fossil fuels. Oil and gas production, which is higher now than at the start of the pandemic (see figures below), can only reach new heights.

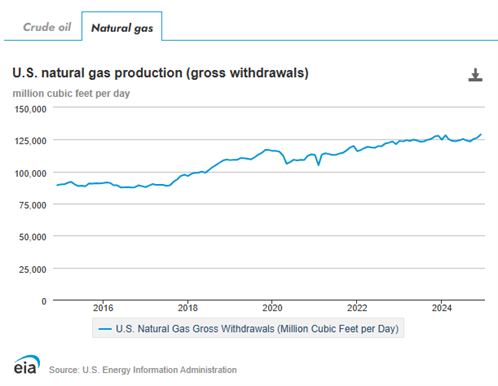
A Good Place To Start
The Trump Administration has signaled that it plans to expand energy production, expedite energy permitting, and ‘roll-back’ regulations and practices that impede growth. As part of this effort, Mr. Trump has named Lee Zeldin, a former GOP member of Congress, to lead the EPA.
Mr. Trump has stated that Mr. Zeldin wishes to “ensure fair and swift deregulatory decisions” while maintaining “the highest environmental standards, including the cleanest air and water on the planet.’’ Further, Elon Musk and Vivek Ramaswamy, heads of the so-called Department of Government Efficiency, or DOGE, have vowed to work with the Trump Administration to use executive action “to pursue three major kinds of reform: regulatory rescissions, administrative reductions and cost savings.”
Trump, Part Two
The second Trump Administration will likely usher in a pitched battle between its attempt to ‘roll-back the Biden Administration’s environmental rules and policies and environmentalists’ defense of those same rules and policies. The outcome is anything but clear.
The Biden Administration still has some time and power to cement its legacy. In this interim transition period, it can, among other things, deny requests for reconsideration of promulgated rules, grant petitions of objection to Title V permits, and seek expedited rulings in multiple court cases across the country. It can also finalize proposed rules and policies. However, those actions can be undone, delayed, or stymied once the Trump Administration assumes control of the EPA and the Department of Justice.
Continue reading “Trump, Part Two”The Right Result for The Sunshine Project
By John B. King (John B. King was a member of Formosa’s legal team, submitting portions of the briefs at the district court and First Circuit.)
The Louisiana First Circuit has issued a sweeping decision affirming and upholding the issuance of air emission permits by the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality (LDEQ) for the Sunshine Project, Formosa’s $9.4 billion petrochemical facility located in St. James Parish (the Facility). RISE St. James, et al v. LDEQ, 23-0578 (La. App. 1 Cir. 1/19/24), — So.3d —, 2024 WL 207859 (the Decision). In doing so, the First Circuit reversed the legally deficient decision of the district court, which had adopted “almost verbatim” the suggested written reasons submitted by the Opponents to the Project.
Continue reading “The Right Result for The Sunshine Project”Enough is Enough
The Corps of Engineers refuses to accept the Supreme Court’s decision in Sackett v. EPA, which substantially reduces the scope of Corps’ jurisdiction over ‘adjacent wetlands.’ The Corps’ “unwillingness to concede its lack of regulatory jurisdiction” prompted the Fifth Circuit to emphatically state “enough is enough” in a recent decision related to adjacent wetlands.
The Clean Water Act regulates the discharge of dredged or fill material into navigable waters. 42 USC §1344(a) (Section 404). Navigable waters are defined as “the waters of the United States, including the territorial seas.” 42 USCA §1362(7).
In Sackett, the Supreme Court held that Corps’ jurisdiction under the Clean Water Act “extends to only those wetlands with a continuous surface connection to bodies that are waters of the United States in their own right, so that they are indistinguishable from those waters.” Sackett, 143 S. Ct. at 1344. The Court also explained that the Corps must establish “first, that the adjacent [body of water constitutes] … ‘water[s] of the United States,’(i.e., a relatively permanent body of water connected to traditional interstate navigable waters); and second, that the wetland has a continuous surface connection with that water, making it difficult to determine where the ‘water’ ends and the ‘wetland’ begins.” Sackett, 143 S. Ct. at 1341.
The Corps has refused to accept this holding and the limitations on its jurisdiction as established by the Supreme Court. The Corps’ current position is that a ‘continuous surface connection’ exists when wetlands are connected to a jurisdictional water by a discrete feature like a non-jurisdictional ditch, swale, pipe, or culvert. Further, a continuous surface connection does not require a constant hydrologic connection. The EPA and Corps echoed this view in guidance released in November 2023 in the form of a PowerPoint presentation.
However, there are two problems with the Corps’ current position. First, the case relied on by the Corps in the November 2023 Guidance does not support its claim. Second, the Fifth Circuit just held that the Corps’ November 2023 Guidance on this point is wrong.
In the November 2023 Guidance, at p. 48, the EPA and the Corps rely on “prior EPA practice” and a Sixth Circuit case, US v. Cundiff, 555 F3d 200 (6 Cir. 2009), for this position. However, that case does not specifically make that statement. The Court actually stated: “Although the term ‘continuous surface connection’ clearly requires surface flow, it does not mean that only perpetually flowing creeks satisfy the plurality’s test.” Cundiff, 555 F3d at p. 212. The Court went on to discuss seasonal flow “and like water bodies.” Waterways with seasonal flow can be relatively permanent waterways. Further, one waterway, the South Channel, provided a continuous surface connection between the wetlands at issue and a traditional waterway (the South Channel had flow for all but a few weeks a year). So, the EPA’s and Corps’ statements regarding non-jurisdictional waters based on Cundiff, if any, are likely dicta.
On Dec. 18, 2023, the Fifth Circuit decided the case of Lewis v. US (2023 WL 8711318), which negates the EPA’s and Corps’ position in the Fifth Circuit. Wetlands on two tracts in Livingston Parish were at issue. The tracts are described as grass-covered, majority dry fields with gravel, logging, and timber roads on the sides of each tract. The owners harvested and managed timber on the tracts. As to the first tract (the east tract), waters flowed through roadside ditches to an unnamed tributary (which flowed intermittently), to Colyell Creek (a relatively permanent waterway), and then to Colyell Bay, a traditional navigble waterway about ten to fifteen miles away. As to the second tract (the west tract), water flowed through roadside ditches to Switch Cane Bayou, to Colyell Creek, and then Colyell Bay.
At the district court level (2020 WL 4798496), the court was reviewing an approved jurisdictional determination (AJD) initially issued in 2017 after an administrative appeal. The 2017 AJD found jurisdictional wetlands, noting the above connections to the traditional navigable waterway. The Plaintiffs argued that there was no jurisdiction under Rapanos (including the Scalia test as to adjacency). At some point in the district court proceedings, the Corps “acknowledged that the land in question does not meet the adjacency requirement set forth under the Scalia test. Accordingly, it provides no basis for CWA jurisdiction.” The district court also found that there was no jurisdiction under the significant nexus test. The matter was remanded back to the Corps.
After remand, the Corps applied the 2020 Navigable Waters Protection Rule to the wetlands on both tracts. The Corps indicated in a 2020 AJD that there were no jurisdictional wetlands on the west tract but found wetlands on the east tract by “connecting (a) roadside ditches and (b) a culvert to (c) an unnamed non-‘relatively permanent water’ tributary, then to (d) Colyell Creek (a ‘relatively permanent water’) several miles away, and ultimately to (e) the traditionally navigable waterway of Colyell Bay ten to fifteen miles from the Lewis property.”
Upon review by the Fifth Circuit and based on these facts, the Court found: “There is no ‘continuous surface connection’ between any plausible wetlands on the Lewis tracts and a ‘relatively permanent body of water connected to traditional interstate navigable waters.’ Recall that the nearest relatively permanent body of water is removed miles away from the Lewis property by roadside ditches, a culvert, and a non-relatively permanent tributary. In sum, it is not difficult to determine where the ‘water’ ends and any ‘wetlands’ on Lewis’s property begin—there is simply no connection whatsoever. There is no factual basis as a matter of law for federal Clean Water Act regulation of these tracts.” Thus, the Fifth Circuit found no continuous surface connection, even though there was a ditch, a culvert, and a non-relatively permanent tributary.
The Lewis decision highlights several important points. First, the Corps admitted under these facts that there was no jurisdiction under the Scalia test in Rapanos (the very same test adopted in Sackett). Second, there was no continuous surface connection even when water may flow through ditches, a culvert, and a non-relatively permanent tributary. Finally, the Sackett holding relating to a determination of where waters ends and wetlands begins was specifically incorporated into the Lewis decision.
As a result of the Lewis decision, non-jurisdictional features (ditches, culverts) and non-relatively permanent waterways are not continuous surface connections and cannot serve to link wetlands on a property to a relatively permanent waterway. On this point, the November 2023 Guidance is not consistent with the Fifth Circuit’s strict and straightforward application of Sackett in the Lewis decision.

